C++ 继承
面向对象程序设计中最重要的一个概念是继承。继承允许我们依据另一个类来定义一个类,这使得创建和维护一个应用程序变得更容易。这样做,也达到了重用代码功能和提高执行效率的效果。
当创建一个类时,您不需要重新编写新的数据成员和成员函数,只需指定新建的类继承了一个已有的类的成员即可。这个已有的类称为基类,新建的类称为派生类。
继承代表了 is a 关系。例如,哺乳动物是动物,狗是哺乳动物,因此,狗是动物,等等。
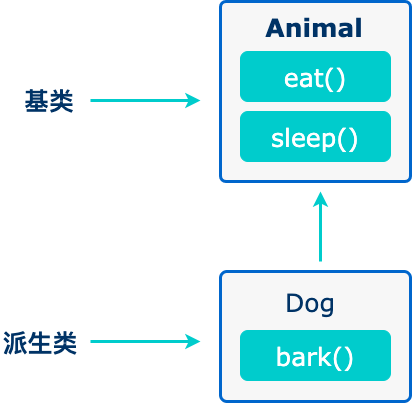
代码如下:
// 基类
class Animal {
// eat() 函数
// sleep() 函数
};
//派生类
class Dog : public Animal {
// bark() 函数
};
基类 & 派生类
一个类可以派生自多个类,这意味着,它可以从多个基类继承数据和函数。定义一个派生类,我们使用一个类派生列表来指定基类。类派生列表以一个或多个基类命名,形式如下:
class derived-class: access-specifier base-class
其中,访问修饰符 access-specifier 是 public、protected 或 private 其中的一个,base-class 是之前定义过的某个类的名称。如果未使用访问修饰符 access-specifier,则默认为 private。
假设有一个基类 Shape,Rectangle 是它的派生类,如下所示:
实例
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
// 基类
class Shape
{
public:
void setWidth(int w)
{
width = w;
}
void setHeight(int h)
{
height = h;
}
protected:
int width;
int height;
};
// 派生类
class Rectangle: public Shape
{
public:
int getArea()
{
return (width * height);
}
};
int main(void)
{
Rectangle Rect;
Rect.setWidth(5);
Rect.setHeight(7);
// 输出对象的面积
cout << "Total area: " << Rect.getArea() << endl;
return 0;
}
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
// 基类
class Shape
{
public:
void setWidth(int w)
{
width = w;
}
void setHeight(int h)
{
height = h;
}
protected:
int width;
int height;
};
// 派生类
class Rectangle: public Shape
{
public:
int getArea()
{
return (width * height);
}
};
int main(void)
{
Rectangle Rect;
Rect.setWidth(5);
Rect.setHeight(7);
// 输出对象的面积
cout << "Total area: " << Rect.getArea() << endl;
return 0;
}当上面的代码被编译和执行时,它会产生下列结果:
Total area: 35
访问控制和继承
派生类可以访问基类中所有的非私有成员。因此基类成员如果不想被派生类的成员函数访问,则应在基类中声明为 private。
我们可以根据访问权限总结出不同的访问类型,如下所示:
| 访问 | public | protected | private |
|---|---|---|---|
| 同一个类 | yes | yes | yes |
| 派生类 | yes | yes | no |
| 外部的类 | yes | no | no |
一个派生类继承了所有的基类方法,但下列情况除外:
- 基类的构造函数、析构函数和拷贝构造函数。
- 基类的重载运算符。
- 基类的友元函数。
继承类型
当一个类派生自基类,该基类可以被继承为 public、protected 或 private 几种类型。继承类型是通过上面讲解的访问修饰符 access-specifier 来指定的。
我们几乎不使用 protected 或 private 继承,通常使用 public 继承。当使用不同类型的继承时,遵循以下几个规则:
- 公有继承(public):当一个类派生自公有基类时,基类的公有成员也是派生类的公有成员,基类的保护成员也是派生类的保护成员,基类的私有成员不能直接被派生类访问,但是可以通过调用基类的公有和保护成员来访问。
- 保护继承(protected): 当一个类派生自保护基类时,基类的公有和保护成员将成为派生类的保护成员。
- 私有继承(private):当一个类派生自私有基类时,基类的公有和保护成员将成为派生类的私有成员。
多继承
多继承即一个子类可以有多个父类,它继承了多个父类的特性。
C++ 类可以从多个类继承成员,语法如下:
class <派生类名>:<继承方式1><基类名1>,<继承方式2><基类名2>,…
{
<派生类类体>
};
其中,访问修饰符继承方式是 public、protected 或 private 其中的一个,用来修饰每个基类,各个基类之间用逗号分隔,如上所示。现在让我们一起看看下面的实例:
实例
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
// 基类 Shape
class Shape
{
public:
void setWidth(int w)
{
width = w;
}
void setHeight(int h)
{
height = h;
}
protected:
int width;
int height;
};
// 基类 PaintCost
class PaintCost
{
public:
int getCost(int area)
{
return area * 70;
}
};
// 派生类
class Rectangle: public Shape, public PaintCost
{
public:
int getArea()
{
return (width * height);
}
};
int main(void)
{
Rectangle Rect;
int area;
Rect.setWidth(5);
Rect.setHeight(7);
area = Rect.getArea();
// 输出对象的面积
cout << "Total area: " << Rect.getArea() << endl;
// 输出总花费
cout << "Total paint cost: $" << Rect.getCost(area) << endl;
return 0;
}
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
// 基类 Shape
class Shape
{
public:
void setWidth(int w)
{
width = w;
}
void setHeight(int h)
{
height = h;
}
protected:
int width;
int height;
};
// 基类 PaintCost
class PaintCost
{
public:
int getCost(int area)
{
return area * 70;
}
};
// 派生类
class Rectangle: public Shape, public PaintCost
{
public:
int getArea()
{
return (width * height);
}
};
int main(void)
{
Rectangle Rect;
int area;
Rect.setWidth(5);
Rect.setHeight(7);
area = Rect.getArea();
// 输出对象的面积
cout << "Total area: " << Rect.getArea() << endl;
// 输出总花费
cout << "Total paint cost: $" << Rect.getCost(area) << endl;
return 0;
}当上面的代码被编译和执行时,它会产生下列结果:
Total area: 35
Total paint cost: $2450