关键词:状态机,售卖机
有限状态机(Finite-State Machine,FSM),简称状态机,是表示有限个状态以及在这些状态之间的转移和动作等行为的数学模型。状态机不仅是一种电路的描述工具,而且也是一种思想方法,在电路设计的系统级和 RTL 级有着广泛的应用。
状态机类型
Verilog 中状态机主要用于同步时序逻辑的设计,能够在有限个状态之间按一定要求和规律切换时序电路的状态。状态的切换方向不但取决于各个输入值,还取决于当前所在状态。状态机可分为 2 类:Moore 状态机和 Mealy 状态机。
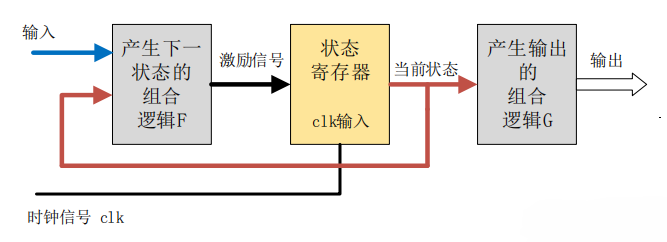
Moore 型状态机
Moore 型状态机的输出只与当前状态有关,与当前输入无关。
输出会在一个完整的时钟周期内保持稳定,即使此时输入信号有变化,输出也不会变化。输入对输出的影响要到下一个时钟周期才能反映出来。这也是 Moore 型状态机的一个重要特点:输入与输出是隔离开来的。
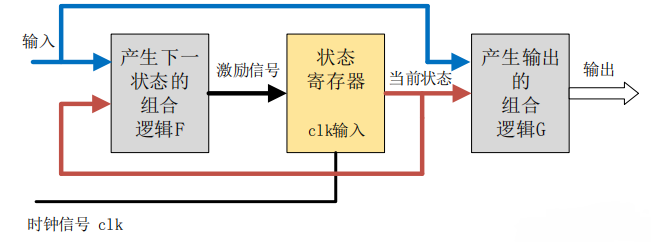
Mealy 型状态机
Mealy 型状态机的输出,不仅与当前状态有关,还取决于当前的输入信号。
Mealy 型状态机的输出是在输入信号变化以后立刻发生变化,且输入变化可能出现在任何状态的时钟周期内。因此,同种逻辑下,Mealy 型状态机输出对输入的响应会比 Moore 型状态机早一个时钟周期。
状态机设计流程
根据设计需求画出状态转移图,确定使用状态机类型,并标注出各种输入输出信号,更有助于编程。一般使用最多的是 Mealy 型 3 段式状态机,下面用通过设计一个自动售卖机的具体实例来说明状态机的设计过程。
自动售卖机
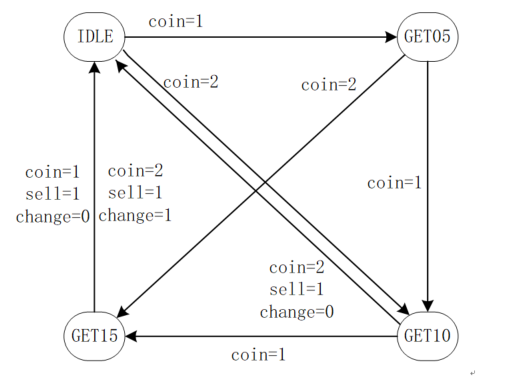
自动售卖机的功能描述如下:
饮料单价 2 元,该售卖机只能接受 0.5 元、1 元的硬币。考虑找零和出货。投币和出货过程都是一次一次的进行,不会出现一次性投入多币或一次性出货多瓶饮料的现象。每一轮售卖机接受投币、出货、找零完成后,才能进入到新的自动售卖状态。
该售卖机的工作状态转移图如下所示,包含了输入、输出信号状态。
其中,coin = 1 代表投入了 0.5 元硬币,coin = 2 代表投入了 1 元硬币。
状态机设计:3 段式(推荐)
状态机设计如下:
- (0) 首先,根据状态机的个数确定状态机编码。利用编码给状态寄存器赋值,代码可读性更好。
- (1) 状态机第一段,时序逻辑,非阻塞赋值,传递寄存器的状态。
- (2) 状态机第二段,组合逻辑,阻塞赋值,根据当前状态和当前输入,确定下一个状态机的状态。
- (3) 状态机第三代,时序逻辑,非阻塞赋值,因为是 Mealy 型状态机,根据当前状态和当前输入,确定输出信号。
实例
// vending-machine
// 2 yuan for a bottle of drink
// only 2 coins supported: 5 jiao and 1 yuan
// finish the function of selling and changing
module vending_machine_p3 (
input clk ,
input rstn ,
input [1:0] coin , //01 for 0.5 jiao, 10 for 1 yuan
output [1:0] change ,
output sell //output the drink
);
//machine state decode
parameter IDLE = 3'd0 ;
parameter GET05 = 3'd1 ;
parameter GET10 = 3'd2 ;
parameter GET15 = 3'd3 ;
//machine variable
reg [2:0] st_next ;
reg [2:0] st_cur ;
//(1) state transfer
always @(posedge clk or negedge rstn) begin
if (!rstn) begin
st_cur <= 'b0 ;
end
else begin
st_cur <= st_next ;
end
end
//(2) state switch, using block assignment for combination-logic
//all case items need to be displayed completely
always @(*) begin
//st_next = st_cur ;//如果条件选项考虑不全,可以赋初值消除latch
case(st_cur)
IDLE:
case (coin)
2'b01: st_next = GET05 ;
2'b10: st_next = GET10 ;
default: st_next = IDLE ;
endcase
GET05:
case (coin)
2'b01: st_next = GET10 ;
2'b10: st_next = GET15 ;
default: st_next = GET05 ;
endcase
GET10:
case (coin)
2'b01: st_next = GET15 ;
2'b10: st_next = IDLE ;
default: st_next = GET10 ;
endcase
GET15:
case (coin)
2'b01,2'b10:
st_next = IDLE ;
default: st_next = GET15 ;
endcase
default: st_next = IDLE ;
endcase
end
//(3) output logic, using non-block assignment
reg [1:0] change_r ;
reg sell_r ;
always @(posedge clk or negedge rstn) begin
if (!rstn) begin
change_r <= 2'b0 ;
sell_r <= 1'b0 ;
end
else if ((st_cur == GET15 && coin ==2'h1)
|| (st_cur == GET10 && coin ==2'd2)) begin
change_r <= 2'b0 ;
sell_r <= 1'b1 ;
end
else if (st_cur == GET15 && coin == 2'h2) begin
change_r <= 2'b1 ;
sell_r <= 1'b1 ;
end
else begin
change_r <= 2'b0 ;
sell_r <= 1'b0 ;
end
end
assign sell = sell_r ;
assign change = change_r ;
endmodule
// vending-machine
// 2 yuan for a bottle of drink
// only 2 coins supported: 5 jiao and 1 yuan
// finish the function of selling and changing
module vending_machine_p3 (
input clk ,
input rstn ,
input [1:0] coin , //01 for 0.5 jiao, 10 for 1 yuan
output [1:0] change ,
output sell //output the drink
);
//machine state decode
parameter IDLE = 3'd0 ;
parameter GET05 = 3'd1 ;
parameter GET10 = 3'd2 ;
parameter GET15 = 3'd3 ;
//machine variable
reg [2:0] st_next ;
reg [2:0] st_cur ;
//(1) state transfer
always @(posedge clk or negedge rstn) begin
if (!rstn) begin
st_cur <= 'b0 ;
end
else begin
st_cur <= st_next ;
end
end
//(2) state switch, using block assignment for combination-logic
//all case items need to be displayed completely
always @(*) begin
//st_next = st_cur ;//如果条件选项考虑不全,可以赋初值消除latch
case(st_cur)
IDLE:
case (coin)
2'b01: st_next = GET05 ;
2'b10: st_next = GET10 ;
default: st_next = IDLE ;
endcase
GET05:
case (coin)
2'b01: st_next = GET10 ;
2'b10: st_next = GET15 ;
default: st_next = GET05 ;
endcase
GET10:
case (coin)
2'b01: st_next = GET15 ;
2'b10: st_next = IDLE ;
default: st_next = GET10 ;
endcase
GET15:
case (coin)
2'b01,2'b10:
st_next = IDLE ;
default: st_next = GET15 ;
endcase
default: st_next = IDLE ;
endcase
end
//(3) output logic, using non-block assignment
reg [1:0] change_r ;
reg sell_r ;
always @(posedge clk or negedge rstn) begin
if (!rstn) begin
change_r <= 2'b0 ;
sell_r <= 1'b0 ;
end
else if ((st_cur == GET15 && coin ==2'h1)
|| (st_cur == GET10 && coin ==2'd2)) begin
change_r <= 2'b0 ;
sell_r <= 1'b1 ;
end
else if (st_cur == GET15 && coin == 2'h2) begin
change_r <= 2'b1 ;
sell_r <= 1'b1 ;
end
else begin
change_r <= 2'b0 ;
sell_r <= 1'b0 ;
end
end
assign sell = sell_r ;
assign change = change_r ;
endmodule
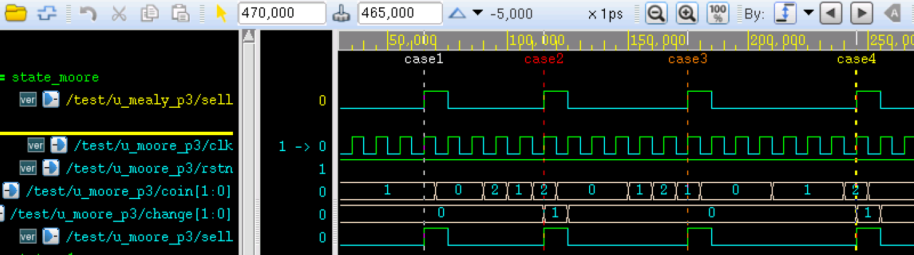
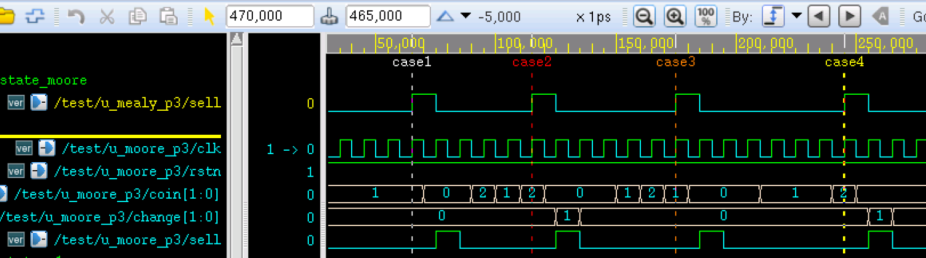
testbench 设计如下。仿真中模拟了 4 种情景,分别是:
case1 对应连续输入 4 个 5 角硬币;case2 对应 1 元 - 5 角 - 1 元的投币顺序;case3 对应 5 角 - 1 元 - 5 角的投币顺序;case4 对应连续 3 个 5 角然后一个 1 元的投币顺序。
实例
`timescale 1ns/1ps
module test ;
reg clk;
reg rstn ;
reg [1:0] coin ;
wire [1:0] change ;
wire sell ;
//clock generating
parameter CYCLE_200MHz = 10 ; //
always begin
clk = 0 ; #(CYCLE_200MHz/2) ;
clk = 1 ; #(CYCLE_200MHz/2) ;
end
//motivation generating
reg [9:0] buy_oper ; //store state of the buy operation
initial begin
buy_oper = 'h0 ;
coin = 2'h0 ;
rstn = 1'b0 ;
#8 rstn = 1'b1 ;
@(negedge clk) ;
//case(1) 0.5 -> 0.5 -> 0.5 -> 0.5
#16 ;
buy_oper = 10'b00_0101_0101 ;
repeat(5) begin
@(negedge clk) ;
coin = buy_oper[1:0] ;
buy_oper = buy_oper >> 2 ;
end
//case(2) 1 -> 0.5 -> 1, taking change
#16 ;
buy_oper = 10'b00_0010_0110 ;
repeat(5) begin
@(negedge clk) ;
coin = buy_oper[1:0] ;
buy_oper = buy_oper >> 2 ;
end
//case(3) 0.5 -> 1 -> 0.5
#16 ;
buy_oper = 10'b00_0001_1001 ;
repeat(5) begin
@(negedge clk) ;
coin = buy_oper[1:0] ;
buy_oper = buy_oper >> 2 ;
end
//case(4) 0.5 -> 0.5 -> 0.5 -> 1, taking change
#16 ;
buy_oper = 10'b00_1001_0101 ;
repeat(5) begin
@(negedge clk) ;
coin = buy_oper[1:0] ;
buy_oper = buy_oper >> 2 ;
end
end
//(1) mealy state with 3-stage
vending_machine_p3 u_mealy_p3 (
.clk (clk),
.rstn (rstn),
.coin (coin),
.change (change),
.sell (sell)
);
//simulation finish
always begin
#100;
if ($time >= 10000) $finish ;
end
endmodule // test
`timescale 1ns/1ps
module test ;
reg clk;
reg rstn ;
reg [1:0] coin ;
wire [1:0] change ;
wire sell ;
//clock generating
parameter CYCLE_200MHz = 10 ; //
always begin
clk = 0 ; #(CYCLE_200MHz/2) ;
clk = 1 ; #(CYCLE_200MHz/2) ;
end
//motivation generating
reg [9:0] buy_oper ; //store state of the buy operation
initial begin
buy_oper = 'h0 ;
coin = 2'h0 ;
rstn = 1'b0 ;
#8 rstn = 1'b1 ;
@(negedge clk) ;
//case(1) 0.5 -> 0.5 -> 0.5 -> 0.5
#16 ;
buy_oper = 10'b00_0101_0101 ;
repeat(5) begin
@(negedge clk) ;
coin = buy_oper[1:0] ;
buy_oper = buy_oper >> 2 ;
end
//case(2) 1 -> 0.5 -> 1, taking change
#16 ;
buy_oper = 10'b00_0010_0110 ;
repeat(5) begin
@(negedge clk) ;
coin = buy_oper[1:0] ;
buy_oper = buy_oper >> 2 ;
end
//case(3) 0.5 -> 1 -> 0.5
#16 ;
buy_oper = 10'b00_0001_1001 ;
repeat(5) begin
@(negedge clk) ;
coin = buy_oper[1:0] ;
buy_oper = buy_oper >> 2 ;
end
//case(4) 0.5 -> 0.5 -> 0.5 -> 1, taking change
#16 ;
buy_oper = 10'b00_1001_0101 ;
repeat(5) begin
@(negedge clk) ;
coin = buy_oper[1:0] ;
buy_oper = buy_oper >> 2 ;
end
end
//(1) mealy state with 3-stage
vending_machine_p3 u_mealy_p3 (
.clk (clk),
.rstn (rstn),
.coin (coin),
.change (change),
.sell (sell)
);
//simulation finish
always begin
#100;
if ($time >= 10000) $finish ;
end
endmodule // test
仿真结果如下:
由图可知,代表出货动作的信号 sell 都能在投币完毕后正常的拉高,而代表找零动作的信号 change 也都能根据输入的硬币场景输出正确的是否找零信号。
状态机修改:2 段式
将 3 段式状态机 2、3 段描述合并,其他部分保持不变,状态机就变成了 2 段式描述。
修改部分如下:
实例
//(2) state switch, and output logic
//all using block assignment for combination-logic
reg [1:0] change_r ;
reg sell_r ;
always @(*) begin //all case items need to be displayed completely
case(st_cur)
IDLE: begin
change_r = 2'b0 ;
sell_r = 1'b0 ;
case (coin)
2'b01: st_next = GET05 ;
2'b10: st_next = GET10 ;
default: st_next = IDLE ;
endcase // case (coin)
end
GET05: begin
change_r = 2'b0 ;
sell_r = 1'b0 ;
case (coin)
2'b01: st_next = GET10 ;
2'b10: st_next = GET15 ;
default: st_next = GET05 ;
endcase // case (coin)
end
GET10:
case (coin)
2'b01: begin
st_next = GET15 ;
change_r = 2'b0 ;
sell_r = 1'b0 ;
end
2'b10: begin
st_next = IDLE ;
change_r = 2'b0 ;
sell_r = 1'b1 ;
end
default: begin
st_next = GET10 ;
change_r = 2'b0 ;
sell_r = 1'b0 ;
end
endcase // case (coin)
GET15:
case (coin)
2'b01: begin
st_next = IDLE ;
change_r = 2'b0 ;
sell_r = 1'b1 ;
end
2'b10: begin
st_next = IDLE ;
change_r = 2'b1 ;
sell_r = 1'b1 ;
end
default: begin
st_next = GET15 ;
change_r = 2'b0 ;
sell_r = 1'b0 ;
end
endcase
default: begin
st_next = IDLE ;
change_r = 2'b0 ;
sell_r = 1'b0 ;
end
endcase
end
//(2) state switch, and output logic
//all using block assignment for combination-logic
reg [1:0] change_r ;
reg sell_r ;
always @(*) begin //all case items need to be displayed completely
case(st_cur)
IDLE: begin
change_r = 2'b0 ;
sell_r = 1'b0 ;
case (coin)
2'b01: st_next = GET05 ;
2'b10: st_next = GET10 ;
default: st_next = IDLE ;
endcase // case (coin)
end
GET05: begin
change_r = 2'b0 ;
sell_r = 1'b0 ;
case (coin)
2'b01: st_next = GET10 ;
2'b10: st_next = GET15 ;
default: st_next = GET05 ;
endcase // case (coin)
end
GET10:
case (coin)
2'b01: begin
st_next = GET15 ;
change_r = 2'b0 ;
sell_r = 1'b0 ;
end
2'b10: begin
st_next = IDLE ;
change_r = 2'b0 ;
sell_r = 1'b1 ;
end
default: begin
st_next = GET10 ;
change_r = 2'b0 ;
sell_r = 1'b0 ;
end
endcase // case (coin)
GET15:
case (coin)
2'b01: begin
st_next = IDLE ;
change_r = 2'b0 ;
sell_r = 1'b1 ;
end
2'b10: begin
st_next = IDLE ;
change_r = 2'b1 ;
sell_r = 1'b1 ;
end
default: begin
st_next = GET15 ;
change_r = 2'b0 ;
sell_r = 1'b0 ;
end
endcase
default: begin
st_next = IDLE ;
change_r = 2'b0 ;
sell_r = 1'b0 ;
end
endcase
end
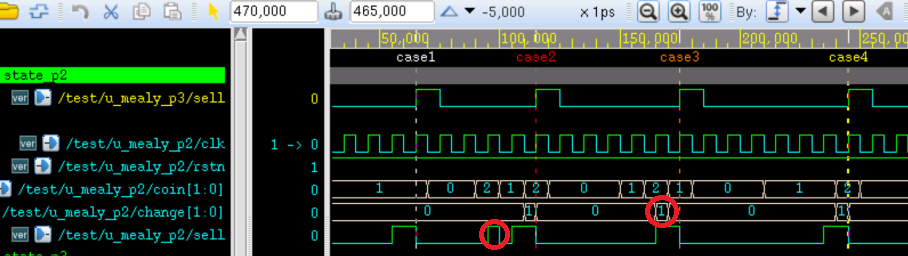
将上述修改的新模块例化到 3 段式的 testbench 中即可进行仿真,结果如下:
由图可知,出货信号 sell 和 找零信号 change 相对于 3 段式状态机输出提前了一个时钟周期,这是因为输出信号都是阻塞赋值导致的。
如图中红色圆圈部分,输出信号都出现了干扰脉冲,这是因为输入信号都是异步的,而且输出信号是组合逻辑输出,没有时钟驱动。
实际中,如果输入信号都是与时钟同步的,这种干扰脉冲是不会出现的。如果是异步输入信号,首先应当对信号进行同步。
状态机修改:1 段式(慎用)
将 3 段式状态机 1、 2、3 段描述合并,状态机就变成了 1 段式描述。
修改部分如下:
实例
//(1) using one state-variable do describe
reg [1:0] change_r ;
reg sell_r ;
always @(posedge clk or negedge rstn) begin
if (!rstn) begin
st_cur <= 'b0 ;
change_r <= 2'b0 ;
sell_r <= 1'b0 ;
end
else begin
case(st_cur)
IDLE: begin
change_r <= 2'b0 ;
sell_r <= 1'b0 ;
case (coin)
2'b01: st_cur <= GET05 ;
2'b10: st_cur <= GET10 ;
endcase
end
GET05: begin
case (coin)
2'b01: st_cur <= GET10 ;
2'b10: st_cur <= GET15 ;
endcase
end
GET10:
case (coin)
2'b01: st_cur <= GET15 ;
2'b10: begin
st_cur <= IDLE ;
sell_r <= 1'b1 ;
end
endcase
GET15:
case (coin)
2'b01: begin
st_cur <= IDLE ;
sell_r <= 1'b1 ;
end
2'b10: begin
st_cur <= IDLE ;
change_r <= 2'b1 ;
sell_r <= 1'b1 ;
end
endcase
default: begin
st_cur <= IDLE ;
end
endcase // case (st_cur)
end // else: !if(!rstn)
end
//(1) using one state-variable do describe
reg [1:0] change_r ;
reg sell_r ;
always @(posedge clk or negedge rstn) begin
if (!rstn) begin
st_cur <= 'b0 ;
change_r <= 2'b0 ;
sell_r <= 1'b0 ;
end
else begin
case(st_cur)
IDLE: begin
change_r <= 2'b0 ;
sell_r <= 1'b0 ;
case (coin)
2'b01: st_cur <= GET05 ;
2'b10: st_cur <= GET10 ;
endcase
end
GET05: begin
case (coin)
2'b01: st_cur <= GET10 ;
2'b10: st_cur <= GET15 ;
endcase
end
GET10:
case (coin)
2'b01: st_cur <= GET15 ;
2'b10: begin
st_cur <= IDLE ;
sell_r <= 1'b1 ;
end
endcase
GET15:
case (coin)
2'b01: begin
st_cur <= IDLE ;
sell_r <= 1'b1 ;
end
2'b10: begin
st_cur <= IDLE ;
change_r <= 2'b1 ;
sell_r <= 1'b1 ;
end
endcase
default: begin
st_cur <= IDLE ;
end
endcase // case (st_cur)
end // else: !if(!rstn)
end
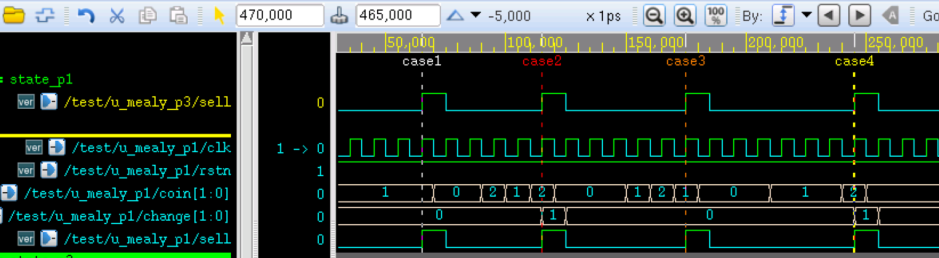
将上述修改的新模块例化到 3 段式的 testbench 中即可进行仿真,结果如下:
由图可知,输出信号与 3 段式状态机完全一致。
1 段式状态机的缺点就是许多种逻辑糅合在一起,不易后期的维护。当状态机和输出信号较少时,可以尝试此种描述方式。
状态机修改:Moore 型
如果使用 Moore 型状态机描述售卖机的工作流程,那么还需要再增加 2 个状态编码,用以描述 Mealy 状态机输出时的输入信号和状态机状态。
3 段式 Moore 型状态机描述的自动售卖机 Verilog 代码如下:
实例
module vending_machine_moore (
input clk ,
input rstn ,
input [1:0] coin , //01 for 0.5 jiao, 10 for 1 yuan
output [1:0] change ,
output sell //output the drink
);
//machine state decode
parameter IDLE = 3'd0 ;
parameter GET05 = 3'd1 ;
parameter GET10 = 3'd2 ;
parameter GET15 = 3'd3 ;
// new state for moore state-machine
parameter GET20 = 3'd4 ;
parameter GET25 = 3'd5 ;
//machine variable
reg [2:0] st_next ;
reg [2:0] st_cur ;
//(1) state transfer
always @(posedge clk or negedge rstn) begin
if (!rstn) begin
st_cur <= 'b0 ;
end
else begin
st_cur <= st_next ;
end
end
//(2) state switch, using block assignment for combination-logic
always @(*) begin //all case items need to be displayed completely
case(st_cur)
IDLE:
case (coin)
2'b01: st_next = GET05 ;
2'b10: st_next = GET10 ;
default: st_next = IDLE ;
endcase
GET05:
case (coin)
2'b01: st_next = GET10 ;
2'b10: st_next = GET15 ;
default: st_next = GET05 ;
endcase
GET10:
case (coin)
2'b01: st_next = GET15 ;
2'b10: st_next = GET20 ;
default: st_next = GET10 ;
endcase
GET15:
case (coin)
2'b01: st_next = GET20 ;
2'b10: st_next = GET25 ;
default: st_next = GET15 ;
endcase
GET20: st_next = IDLE ;
GET25: st_next = IDLE ;
default: st_next = IDLE ;
endcase // case (st_cur)
end // always @ (*)
// (3) output logic,
// one cycle delayed when using non-block assignment
reg [1:0] change_r ;
reg sell_r ;
always @(posedge clk or negedge rstn) begin
if (!rstn) begin
change_r <= 2'b0 ;
sell_r <= 1'b0 ;
end
else if (st_cur == GET20 ) begin
sell_r <= 1'b1 ;
end
else if (st_cur == GET25) begin
change_r <= 2'b1 ;
sell_r <= 1'b1 ;
end
else begin
change_r <= 2'b0 ;
sell_r <= 1'b0 ;
end
end
assign sell = sell_r ;
assign change = change_r ;
endmodule
module vending_machine_moore (
input clk ,
input rstn ,
input [1:0] coin , //01 for 0.5 jiao, 10 for 1 yuan
output [1:0] change ,
output sell //output the drink
);
//machine state decode
parameter IDLE = 3'd0 ;
parameter GET05 = 3'd1 ;
parameter GET10 = 3'd2 ;
parameter GET15 = 3'd3 ;
// new state for moore state-machine
parameter GET20 = 3'd4 ;
parameter GET25 = 3'd5 ;
//machine variable
reg [2:0] st_next ;
reg [2:0] st_cur ;
//(1) state transfer
always @(posedge clk or negedge rstn) begin
if (!rstn) begin
st_cur <= 'b0 ;
end
else begin
st_cur <= st_next ;
end
end
//(2) state switch, using block assignment for combination-logic
always @(*) begin //all case items need to be displayed completely
case(st_cur)
IDLE:
case (coin)
2'b01: st_next = GET05 ;
2'b10: st_next = GET10 ;
default: st_next = IDLE ;
endcase
GET05:
case (coin)
2'b01: st_next = GET10 ;
2'b10: st_next = GET15 ;
default: st_next = GET05 ;
endcase
GET10:
case (coin)
2'b01: st_next = GET15 ;
2'b10: st_next = GET20 ;
default: st_next = GET10 ;
endcase
GET15:
case (coin)
2'b01: st_next = GET20 ;
2'b10: st_next = GET25 ;
default: st_next = GET15 ;
endcase
GET20: st_next = IDLE ;
GET25: st_next = IDLE ;
default: st_next = IDLE ;
endcase // case (st_cur)
end // always @ (*)
// (3) output logic,
// one cycle delayed when using non-block assignment
reg [1:0] change_r ;
reg sell_r ;
always @(posedge clk or negedge rstn) begin
if (!rstn) begin
change_r <= 2'b0 ;
sell_r <= 1'b0 ;
end
else if (st_cur == GET20 ) begin
sell_r <= 1'b1 ;
end
else if (st_cur == GET25) begin
change_r <= 2'b1 ;
sell_r <= 1'b1 ;
end
else begin
change_r <= 2'b0 ;
sell_r <= 1'b0 ;
end
end
assign sell = sell_r ;
assign change = change_r ;
endmodule
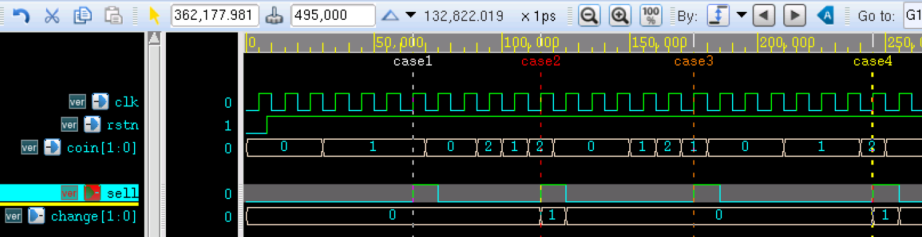
将上述修改的 Moore 状态机例化到 3 段式的 testbench 中即可进行仿真,结果如下:
由图可知,输出信号与 Mealy 型 3 段式状态机相比延迟了一个时钟周期,这是因为进入到新增加的编码状态机时需要一个时钟周期的时延。此时,输出再用非阻塞赋值就会导致最终的输出信号延迟一个时钟周期。这也属于 Moore 型状态机的特点。
输出信号赋值时,用阻塞赋值,则可以提前一个时钟周期。
输出逻辑修改如下。
实例
// (3.2) output logic, using block assignment
reg [1:0] change_r ;
reg sell_r ;
always @(*) begin
change_r = 'b0 ;
sell_r = 'b0 ; //not list all condition, initializing them
if (st_cur == GET20 ) begin
sell_r = 1'b1 ;
end
else if (st_cur == GET25) begin
change_r = 2'b1 ;
sell_r = 1'b1 ;
end
end
// (3.2) output logic, using block assignment
reg [1:0] change_r ;
reg sell_r ;
always @(*) begin
change_r = 'b0 ;
sell_r = 'b0 ; //not list all condition, initializing them
if (st_cur == GET20 ) begin
sell_r = 1'b1 ;
end
else if (st_cur == GET25) begin
change_r = 2'b1 ;
sell_r = 1'b1 ;
end
end
输出信号阻塞赋值的仿真结果如下:
由图可知,输出信号已经和 3 段式 Mealy 型状态机一致。