C++ for 循环
for 循环允许您编写一个执行特定次数的循环的重复控制结构。
语法
C++ 中 for 循环的语法:
for ( init; condition; increment )
{
statement(s);
}
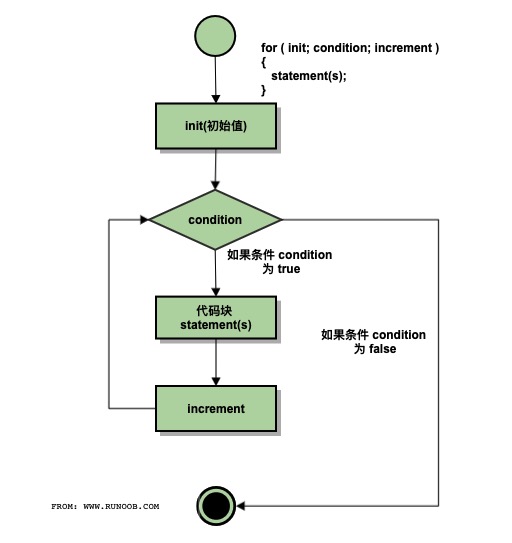
下面是 for 循环的控制流:
- init 会首先被执行,且只会执行一次。这一步允许您声明并初始化任何循环控制变量。您也可以不在这里写任何语句,只要有一个分号出现即可。
- 接下来,会判断 condition。如果为真,则执行循环主体。如果为假,则不执行循环主体,且控制流会跳转到紧接着 for 循环的下一条语句。
- 在执行完 for 循环主体后,控制流会跳回上面的 increment 语句。该语句允许您更新循环控制变量。该语句可以留空,只要在条件后有一个分号出现即可。
- 条件再次被判断。如果为真,则执行循环,这个过程会不断重复(循环主体,然后增加步值,再然后重新判断条件)。在条件变为假时,for 循环终止。
流程图
实例
实例
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main ()
{
// for 循环执行
for( int a = 10; a < 20; a = a + 1 )
{
cout << "a 的值:" << a << endl;
}
return 0;
}
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main ()
{
// for 循环执行
for( int a = 10; a < 20; a = a + 1 )
{
cout << "a 的值:" << a << endl;
}
return 0;
}当上面的代码被编译和执行时,它会产生下列结果:
a 的值: 10
a 的值: 11
a 的值: 12
a 的值: 13
a 的值: 14
a 的值: 15
a 的值: 16
a 的值: 17
a 的值: 18
a 的值: 19
基于范围的for循环(C++11)
for 语句允许简单的范围迭代:
int my_array[5] = {1, 2, 3, 4, 5};
// 每个数组元素乘于 2
for (int &x : my_array)
{
x *= 2;
cout << x << endl;
}
// auto 类型也是 C++11 新标准中的,用来自动获取变量的类型
for (auto &x : my_array) {
x *= 2;
cout << x << endl;
}上面for述句的第一部分定义被用来做范围迭代的变量,就像被声明在一般for循环的变量一样,其作用域仅只于循环的范围。而在":"之后的第二区块,代表将被迭代的范围。
实例
#include<iostream>
#include<string>
#include<cctype>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
string str("some string");
// range for 语句
for(auto &c : str)
{
c = toupper(c);
}
cout << str << endl;
return 0;
}
#include<iostream>
#include<string>
#include<cctype>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
string str("some string");
// range for 语句
for(auto &c : str)
{
c = toupper(c);
}
cout << str << endl;
return 0;
}上面的程序使用Range for语句遍历一个字符串,并将所有字符全部变为大写,然后输出结果为:
SOME STRING